It is critical to establish an effective Human Resource (HR) team structure in the ever-changing world of modern company. An organization’s success is greatly impacted by the way it handles its staff. In addition to streamlining operations, a well-designed HR team structure develops talent, increases employee satisfaction, and guarantees regulatory compliance. Now let’s explore the core ideas and models for building a strong HR department that supports company objectives and makes the most of its workforce.
Core functions of an HR team
- Recruitment and selection: The key to any organization’s success is hiring and employing outstanding personnel. The recruitment process is managed by a committed staff, which also handles applicant sourcing, interviewing, and onboarding.
- Training and development: Employee development and organizational agility depend on ongoing education and skill improvement. The training and development team develops and implements programs to foster potential and improve leadership abilities.
- Employee relations: Keeping morale high and output high requires fostering a positive work environment and handling employee complaints. The employee relations staff is in charge of ensuring effective communication and conflict resolution.
- Pay and benefits: Attracting and keeping talent requires competitive pay packages that are both fair. The compensation and benefits team is in charge of creating and managing salary structures, bonuses, and other benefits.
- Compliance and risk management: To stay out of legal hot water, it’s critical to stay current on labor laws and regulations. The compliance team reduces the risks related to employment practices and makes sure that HR procedures comply with legal standards.

Factors affecting the structure of the HR team
- Size of the oganization: While larger firms may choose to use specialist roles to perform a variety of functions, smaller businesses may have a lean HR team with generalists wearing numerous hats.
- Industry-specific requirements: Sectors with distinct HR requirements, such as banking or healthcare, may have strict compliance laws or require particular training initiatives.
- Workforce distribution by geography: Decentralized HR systems may be necessary for organizations with distributed teams to efficiently address local demands.
- Organizational culture and management style: Whether the organization is more collaborative or hierarchical in nature, HR structures should be in line with its values and leadership philosophy.
Sample HR team structures
- Decentralized vs. centralized models: Decentralized models assign HR duties to specific departments or areas in order to provide more flexibility and response, whereas centralized models combine HR services under one roof for uniformity and efficiency.
- Specialist vs. generalist models: Specialist models place more emphasis on in-depth knowledge in particular domains like compliance, training, or recruitment than generalist models do on hiring HR experts with wide expertise across several functions.
- Hybrid models: To achieve a balance between standardization and customization, hybrid models mix aspects of centralized and decentralized organizations or combine generalist and specialized positions.
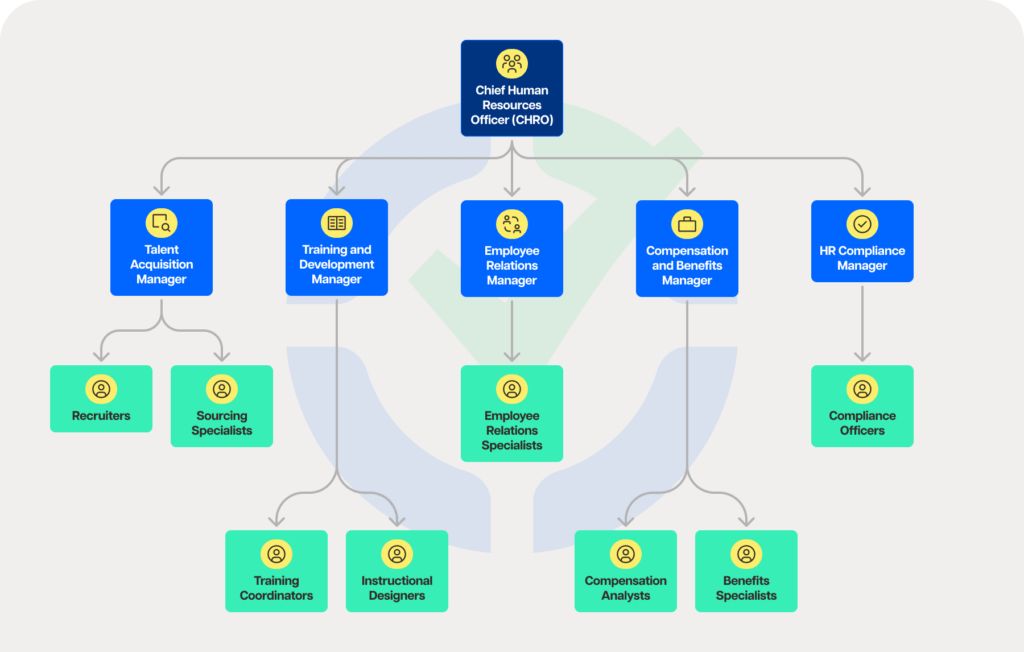
Creating an efficient HR team structure
- Aligning with organizational goals: To promote alignment and synergy across departments, HR initiatives should be in line with the larger business objectives.
- Balancing flexibility and specialization: Maintaining flexibility and specialization: The agility and expertise of the HR staff are ensured by finding the ideal balance between flexible generalists and specialized experts.
- Importance of communication and collaboration: The significance of communication and cooperation lies in their ability to promote teamwork and synergy, which empowers HR professionals to effectively tackle obstacles and seize opportunities.
- Using technology to increase efficiency: Using HR technologies helps to improve data-driven decision-making, expedite procedures, and free up time for strategic projects.

Implementing changes to the HR structure
- Evaluate current HR capabilities: Make a comprehensive evaluation of current HR capabilities, noting their advantages, disadvantages, and potential areas for development.
- How to reorganize the HR staff: Create a phased plan that addresses restructuring, including stakeholders, effectively conveying changes, and offering required assistance and training.
- Monitoring and assessing impact: Ask for input, examine data, and make necessary modifications to maximize performance as you continue to assess the new HR structure’s efficacy.
Conclusion
The importance of having a productive HR team structure cannot be emphasized enough. HR departments can unleash the full potential of their workforce through leveraging technology, promoting communication and cooperation, balancing freedom and specialization, and aligning with business goals. HR structures must change along with businesses, embracing innovation and adjusting to changing needs in order to stay competitive in the ever-changing industry.

Andy is a technology & marketing leader who has delivered award-winning and world-first experiences.


